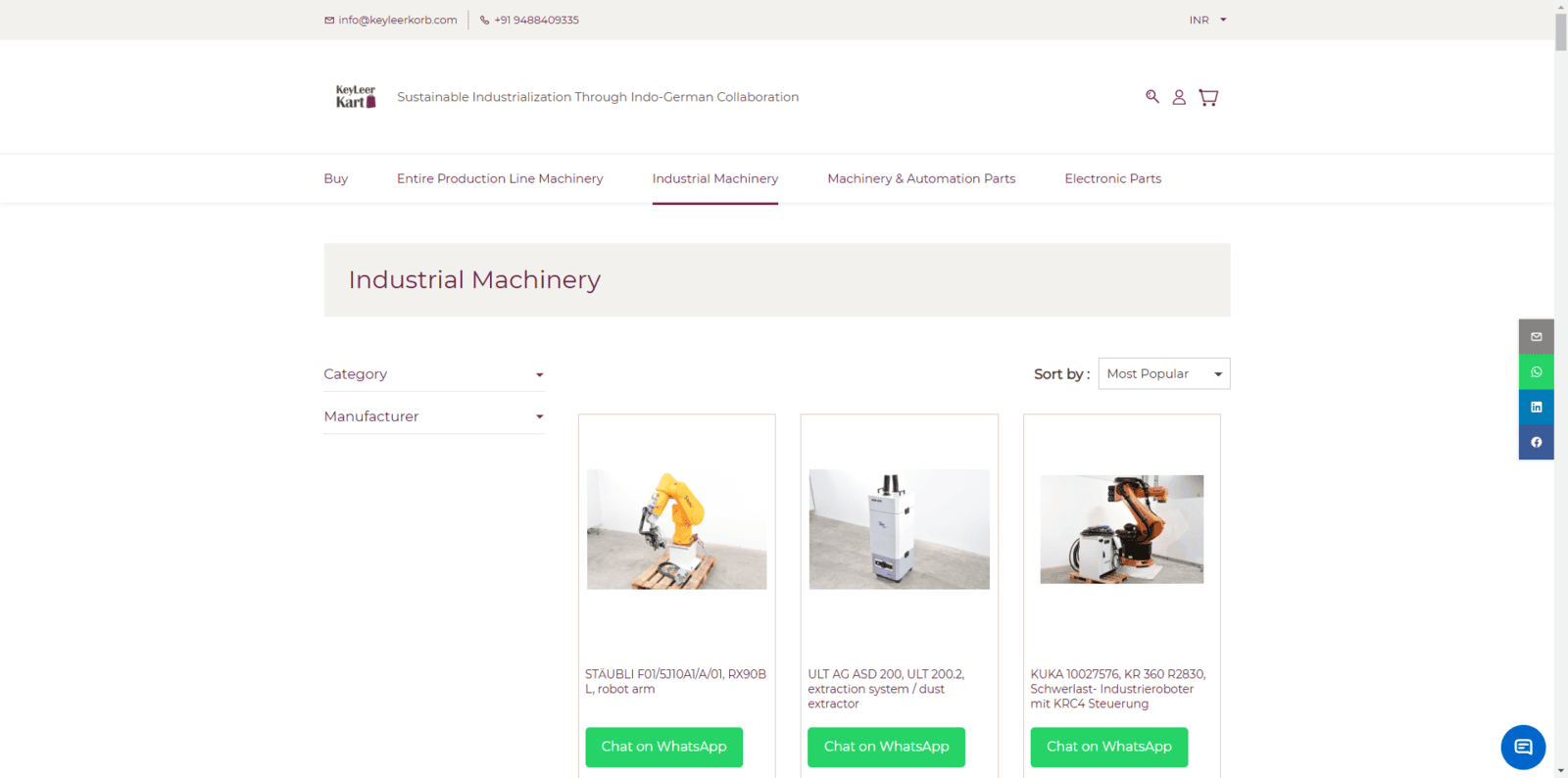
The used machinery market in India is booming, with many businesses opting for cost-effective, high-quality second-hand equipment, especially CNC machines and industrial machinery imported from countries like Germany. However, purchasing used machinery involves more than just finding the right machine at the right price. There are several legal considerations that Indian buyers must be aware of to ensure a smooth and compliant transaction. This blog will guide you through the key legal aspects, supported by statistics, reports, and credible sources.
1. Understanding Import Regulations
Customs Duties and Taxes
When importing used machinery into India, buyers must comply with customs regulations. The Indian government imposes customs duties, GST, and other taxes on imported machinery. According to the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC), the customs duty on used machinery typically ranges between 7.5% to 10%, depending on the type of equipment and its age.
Key Tip: Always check the latest customs duty rates on the official CBIC website: https://www.cbic.gov.in.
Restrictions on Age of Machinery
The Indian government has specific rules regarding the age of used machinery that can be imported. As per the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT), machinery older than 10 years requires special permission and a technical evaluation report to ensure it meets safety and environmental standards.
Reference: DGFT Notification on Import of Second-Hand Machinery: https://dgft.gov.in.
2. Compliance with Environmental and Safety Standards
Pollution Control Norms
Used machinery must comply with India’s environmental regulations, particularly those set by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB). Buyers must ensure that the machinery does not emit excessive pollutants or violate noise standards.
Key Tip: Check the CPCB guidelines for industrial machinery: https://cpcb.nic.in.
Safety Certifications
Machinery imported into India must meet safety standards set by organizations like the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). For example, CNC machines must adhere to IS 13276 standards for safety and performance.
Reference: BIS Standards for Machinery: https://bis.gov.in.
3. Documentation and Legal Formalities
Bill of Entry and Commercial Invoice
When importing used machinery, you must submit a Bill of Entry and a Commercial Invoice to customs. These documents should include details like the machine’s value, age, and specifications.
Technical Evaluation Report
For machinery older than 10 years, a Technical Evaluation Report from an authorized agency is mandatory. This report confirms that the machine is in working condition and complies with Indian standards.
Key Tip: Use authorized agencies like the Engineering Export Promotion Council (EEPC) for technical evaluations: https://www.eepcindia.org.
4. Intellectual Property Rights (IPR)
Avoiding Counterfeit Machinery
Buyers must ensure that the used machinery they purchase does not infringe on intellectual property rights. Counterfeit or illegally replicated machinery can lead to legal disputes and financial losses.
Key Tip: Verify the authenticity of the machinery with the manufacturer or authorized dealers.
5. Warranty and After-Sales Support
Warranty Claims
Unlike new machinery, used machinery may not come with a manufacturer’s warranty. Buyers should negotiate warranty terms with the seller and ensure that the machine is thoroughly inspected before purchase.
After-Sales Service
Ensure that the seller provides reliable after-sales support, including spare parts and maintenance services. This is especially important for imported machinery, as sourcing parts locally can be challenging.
6. Legal Disputes and Dispute Resolution
Contractual Agreements
Always sign a detailed contract with the seller, outlining the terms of sale, payment, delivery, and liability. This contract should be legally vetted to avoid future disputes.
Arbitration and Mediation
In case of disputes, buyers can opt for arbitration or mediation through organizations like the Indian Council of Arbitration (ICA).
Reference: ICA Dispute Resolution Services: https://www.icaindia.co.in.
7. Recent Trends and Statistics
Growth in Used Machinery Imports
According to a report by Statista, the Indian used machinery market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for cost-effective manufacturing solutions.
Reference: Statista Report on Indian Machinery Market: https://www.statista.com.
Government Initiatives
The Indian government’s Make in India initiative has encouraged the import of high-quality used machinery to boost domestic manufacturing. This has led to a surge in imports from countries like Germany, Japan, and Italy.
Reference: Make in India Official Website: https://www.makeinindia.com.
8. Tips for Indian Buyers
Work with Reputable Sellers: Partner with trusted sellers who have a proven track record of supplying quality used machinery.
Verify Documentation: Ensure all legal documents, including invoices, certificates, and technical reports, are in order.
Consult Legal Experts: Seek advice from legal experts specializing in trade and import regulations.
Plan for Logistics: Factor in shipping, customs clearance, and installation costs when budgeting for used machinery.
Conclusion
Buying used machinery, especially imported CNC machines, can be a game-changer for Indian businesses looking to reduce costs and improve efficiency. However, it is crucial to navigate the legal landscape carefully to avoid pitfalls. By understanding customs regulations, environmental norms, and contractual obligations, buyers can make informed decisions and ensure a hassle-free transaction.
For more information on high-quality used machinery from Germany, visit our e-commerce platform: www.keyleerkart.in . We specialize in providing reliable, inspected, and legally compliant used machinery to help your business thrive.
References and Further Reading
Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC): https://www.cbic.gov.in
Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT): https://dgft.gov.in
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB): https://cpcb.nic.in
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS): https://bis.gov.in
Statista Report on Indian Machinery Market: https://www.statista.com
Make in India Initiative: https://www.makeinindia.com